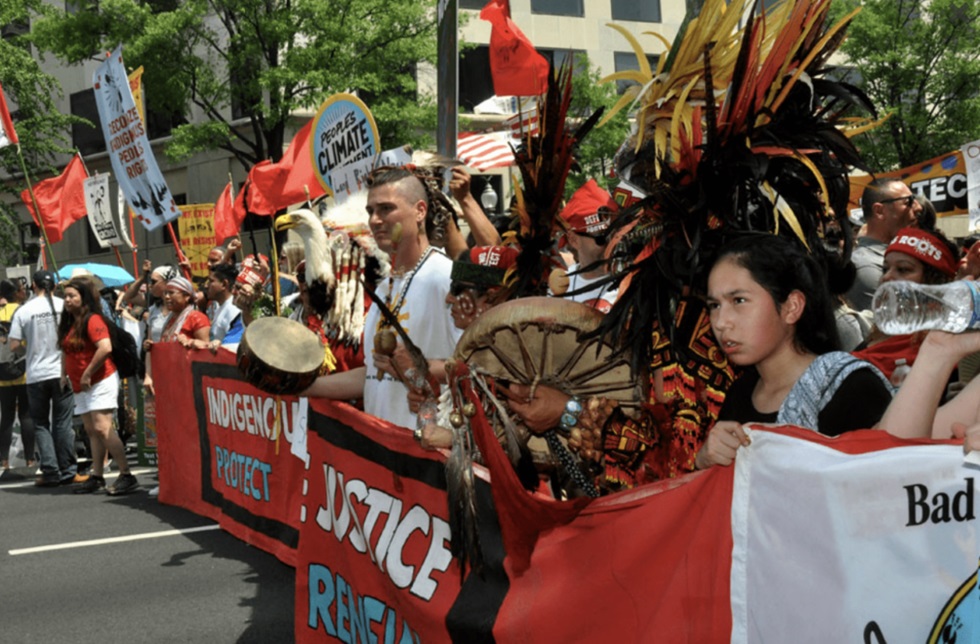
The Line 5 oil pipeline that snakes through Wisconsin and Michigan won a key permit this month: pending federal studies and approvals, Canada-based Enbridge Energy will build a new section of pipeline and tunnel underneath the Great Lakes despite widespread Indigenous opposition. You may not have heard of Line 5, but over the next few years, the controversy surrounding the 645-mile pipeline is expected to intensify.
The 70-year-old pipeline stretches from Superior, Wisconsin, through Michigan to Sarnia, Ontario, transporting up to 540,000 gallons of oil and natural gas liquids per day. It’s part of a network of more than 3,000 miles of pipelines that the company operates throughout the U.S. and Canada, including the Line 3 pipeline in Minnesota where hundreds of opponents were arrested or cited in 2021 for protesting construction, including citizens and members of the Red Lake Band of Chippewa Indians and White Earth Band of Ojibwe.
Now, Enbridge Energy, with the support of the Canadian government, is seeking approvals to build a new $500 million conduit to replace an underwater section of Line 5 in the Straits of Mackinac, while facing lawsuits backed by dozens of Indigenous nations as well as the state of Michigan.
A key concern is the aging pipeline’s risk to the Great Lakes, which represent more than a fifth of the world’s fresh surface water. Environmental concerns are so great that three years ago, Michigan Governor Gretchen Whitmer ordered Enbridge’s dual pipelines that run for 4 miles at the bottom of the Straits of Mackinac to cease operations.
“The state is revoking the easement for violation of the public trust doctrine, given the unreasonable risk that continued operation of the dual pipelines poses to the Great Lakes,” the governor’s office said at the time.
The move came just a year after the Bad River Band tribal nation filed a lawsuit against Enbridge regarding another, separate section of Line 5 in Wisconsin located across 12 miles of the Bad River reservation. The pipeline had been installed in 1953 and, at the time, had received easements to do so from the Bureau of Indian Affairs.
But the easements expired, and in a court filing, the tribal nation said the company “has continued to operate the pipeline as if it has an indefinite entitlement to do so,” despite federal law that bans the renewal of expired right-of-way permits on Indian land and would require Enbridge to obtain new permits and approvals from the Band.
The Bad River won a key victory last summer when a Wisconsin judge ruled that the company must shut down the portion of its pipeline that trespasses on the reservation by 2026.
Enbridge has resisted calls to cease Line 5 operations. Instead, the company contends that it has the right to continue operating there, citing a 1992 agreement with the Band, and is planning to reroute the pipeline while appealing the Wisconsin judge’s decision. The company also argues that building a new pipeline 100 feet below the lake bed through the Straits of Mackinac will virtually eliminate the chance of a spill.
“Line 5 poses little risk to natural and cultural resources, nor does it endanger the way of life of Indigenous communities,” company spokesperson Ryan Duffy said. “Line 5 is operated safely and placing the line in a tunnel well below the lake bed at the Straits of Mackinac will only serve to make a safe pipeline safer.”
To that end, Enbridge successfully appeared before the Michigan Public Service Commission, the state’s top energy regulator, this month and got permission to build a new concrete tunnel beneath the channel connecting Lake Michigan and Lake Huron. The commission cited the need for the light crude oil and natural gas liquids that the pipeline transports, and said other alternatives like driving, trucking or hauling by barge or rail would increase the risk of a spill.
The commission’s approval contradicts Governor Whitmer’s efforts to shut down the pipeline. In the wake of the permit, the governor’s office told reporters the state commission is “independent.” Both of the governor’s appointees on the board voted in favor of the permit.
The approval doesn’t mean that the project will proceed, but it is encouraging for the company as it seeks federal clearance. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers is in the process of putting together a draft environmental impact statement for the project. That document isn’t expected to be published until spring 2025.
In the meantime, Line 5 has gotten lots of support from the government of Canada, where Enbridge Energy is based. The government has repeatedly invoked a 1977 energy treaty between the U.S. and Canada to defend the pipeline.
That’s frustrating to Indigenous peoples who have seen their treaty rights repeatedly violated.
“What we’re simply trying to continue to preserve and protect is an Indigenous way of life, which is the same thing our ancestors tried to preserve and protect when they first entered into those treaty negotiations,” said Whitney Gravelle, chairperson of the Bay Mills Indian Community, one of numerous tribal nations opposing Line 5.
The Straits are also the site of Anishinaabe creation stories, the waters from which the Great Turtle emerged to create Turtle Island, what is currently called North America. Gravelle said that maintaining clean lakes where Indigenous people can fish is about more than just the right to fish. It’s about the continuation of culture.
“It’s about being able to learn from your parents and your elders about what fishing means to your people, whether it be in ceremony or in tradition or in oral storytelling, and then understanding the role that that fish plays in your community,” she said.
Last summer, José Francisco Calí Tzay, United Nations special rapporteur on the rights of Indigenous Peoples, called for suspending the pipeline’s operations “until the free, prior, and informed consent of the Indigenous Peoples affected is secured.” Free, prior, and informed consent is a right guaranteed to Indigenous Peoples under international law that says governments must consult Indigenous nations in good faith to obtain their consent before undertaking projects that affect their land and resources — consent that Bad River, for instance, has refused to give.
“Canada is advocating for the pipeline to continue operations, following the decision of a Parliamentary Committee that did not hear testimony from the affected Indigenous Peoples,” Calí Tzay wrote, adding the country’s support for the pipeline contradicts its international commitments to mitigate climate change in addition to the risk of a “catastrophic spill.”
Part of what makes Line 5 such a flashpoint is the importance of the Great Lakes and Enbridge’s spotty environmental record. As the Guardian reported last month, the Great Lakes “stretch out beyond horizons, collectively covering an area as large as the U.K. and providing drinking water for a third of all Canadians and one in 10 Americans.”
In 2010, two separate pipelines run by Enbridge ruptured, spilling more than a million gallons of oil between them into rivers in Michigan and Illinois. The Environmental Protection Agency found that Enbridge was at fault not only for failing to upkeep the pipeline but also for restarting the pipeline after alarms went off without checking whether it failed. The company eventually reached a $177 million settlement with federal regulators over the disaster.
A 2017 National Wildlife Federation analysis found that Line 5 has leaked more than a million gallons on 29 separate occasions. The company said just five of these instances were outside of Enbridge facilities, and that no spills have occurred in the Straits of Mackinac or on the Bad River Reservation. Still, the section of the pipeline on the floor of the Straits of Mackinac has been dented by boat anchors dropped in the lakes, including from Enbridge-contracted vessels.
Despite Indigenous peoples’ concerns, Line 5 continues to gain momentum, in part because of the amount of energy it supplies to the U.S. and Canada and the countries’ continued dependence on fossil fuels. While the international community agreed to curb fossil fuels this month at COP28, there’s no agreed-upon timeline for actually doing so, and the consumer demand for affordable energy remains high, especially in light of inflation driving the prices of food and housing.
Meanwhile, more than 60 tribal nations, including every federally recognized tribe in Michigan, have said the pipeline poses “an unacceptable risk of an oil spill into the Great Lakes.”
“The Straits of Mackinac are a sacred wellspring of life and culture for tribal nations in Michigan and beyond,” the nations wrote in an amicus brief supporting a lawsuit challenging the pipeline.
To Gravelle from the Bay Mills Indian Community, the issue is deeply personal and goes beyond maintaining access to clean water and the ability to fish safely. Fishing is deeply intertwined with her peoples’ culture. When a baby is born, their first meal is fish, and when her people hold traditional ceremonies, they serve fish.
“Our traditions and who we are as a people are all wrapped up into what we do with fish,” Gravelle said. “Our relationship with the land and water is more important than any commercial value that could ever be realized from an oil pipeline.”
This article was reposted from Grist.org.
We hope you appreciated this article. At People’s World, we believe news and information should be free and accessible to all, but we need your help. Our journalism is free of corporate influence and paywalls because we are totally reader-supported. Only you, our readers and supporters, make this possible. If you enjoy reading People’s World and the stories we bring you, please support our work by donating or becoming a monthly sustainer today. Thank you!